Storage Technology Overview
Storage Drive Speed Differences and Ideal Use Cases
Modern computer storage technology offers three primary options, each with distinct performance characteristics and costs. Understanding the differences and ideal use cases for Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and NVMe drives is really helpful when making decisions about what hardware to buy for a homelab application.
Complete Storage Drive Comparison
| Storage Type | Sequential Read (MB/s) | Sequential Write (MB/s) | Random Read IOPS | Cost per GB (USD) | Power Active (W) | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDD (7200 RPM) | 80-160 | 80-160 | 100-200 | $0.010-0.015 | 6-9 | Mass storage, backup & archive, media libraries, surveillance systems |
| SATA SSD | 500-550 | 450-520 | 90K-100K | $0.08-0.10 | 2-3 | General computing, gaming, boot drives, laptops, budget upgrades |
| NVMe PCIe 3.0 | 2,000-3,500 | 1,800-3,000 | 400K-600K | $0.10-0.15 | 3-5 | High-performance gaming, content creation, workstations |
| NVMe PCIe 4.0 | 5,000-7,000 | 4,000-7,000 | 800K-1M | $0.12-0.18 | 4-8 | Professional workstations, video editing, server applications |
| NVMe PCIe 5.0 | 12,000-14,000 | 7,000-10,000 | 2M-2.7M | $0.15-0.25 | 6-10 | Cutting-edge workstations, 8K video editing, enterprise servers |
Performance Speed Analysis
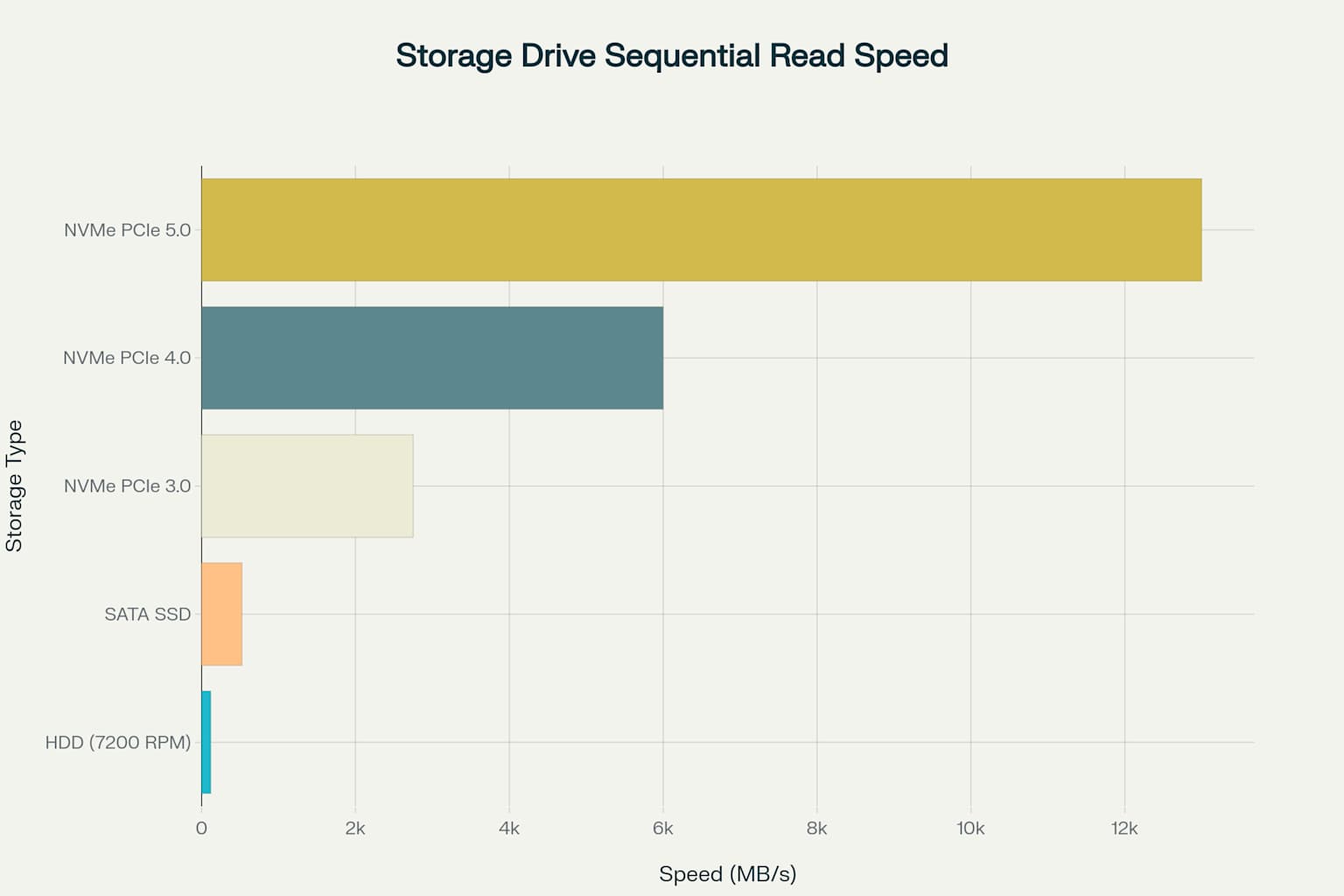
The speed differences between storage technologies are pretty dramatic and represent significant performance tiers12. Traditional HDDs operate at 80-160 MB/s for both read and write operations, limited by their mechanical spinning disks and mechanical read/write head3. SATA SSDs provide a substantial improvement, reaching 500-550 MB/s read speeds, representing approximately 3-4x faster performance than HDDs42.
NVMe drives showcase even more impressive performance gains. These drives basically plug straight into the PCI data bus giving blazing fast transfers. PCIe 3.0 NVMe drives deliver 2,000-3,500 MB/s read speeds, while PCIe 4.0 variants reach 5,000-7,000 MB/s56. The latest PCIe 5.0 NVMe drives achieve remarkable speeds of 12,000-14,000 MB/s, making them up to 100x faster than traditional HDDs76.
Cost Considerations
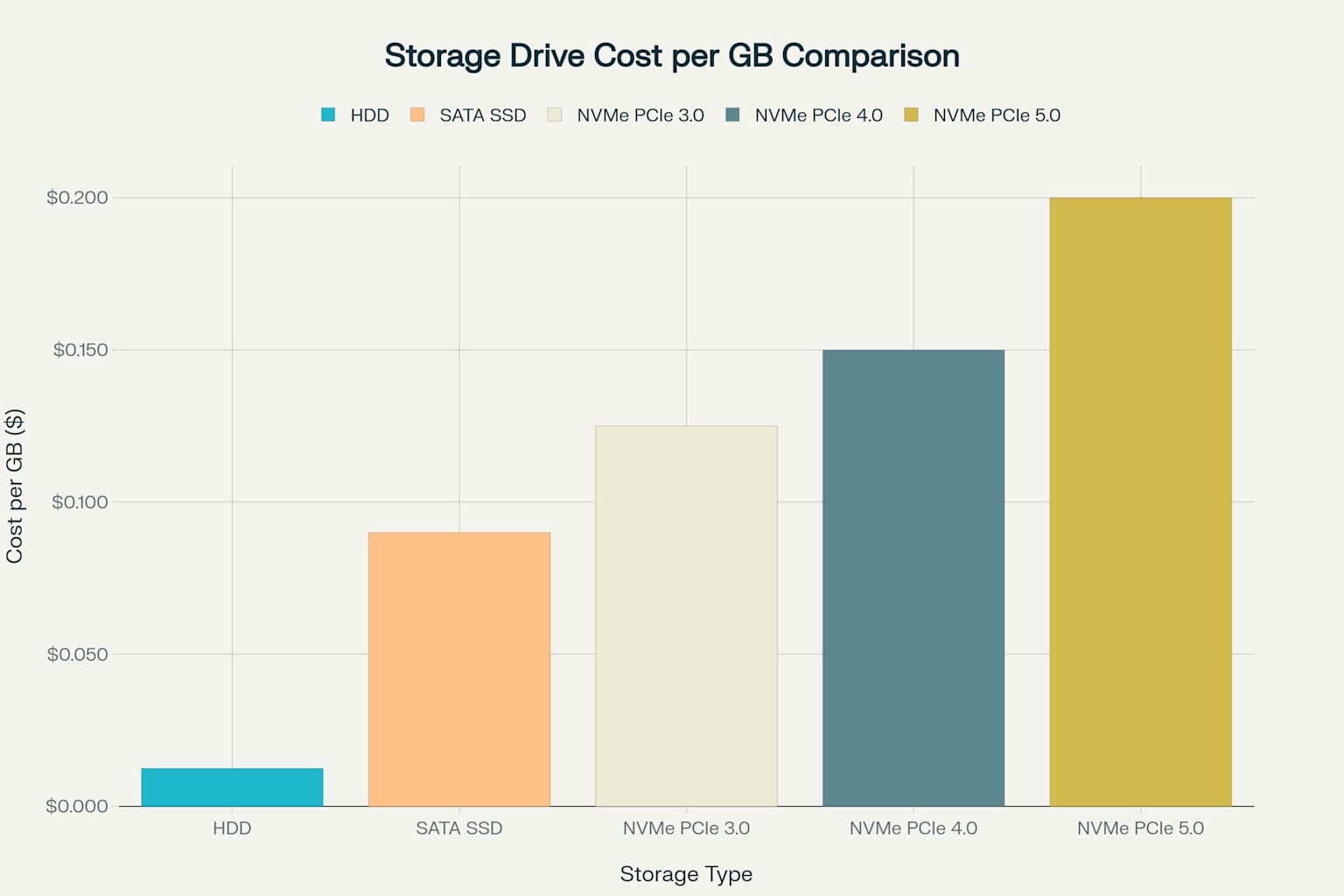
Storage cost per gigabyte varies significantly across technologies, with HDDs offering the most economical solution at approximately $0.010-0.015 per GB89. SATA SSDs cost around $0.08-0.10 per GB, while NVMe drives range from $0.10-0.25 per GB depending on the PCIe generation1011. This price differential matches the performance differential somewhat meaning when it comes to performance, you pretty much get what you pay for. But before you go dropping a paycheque on storage, make sure the system you will plug it into supports the technology you intend to buy or your costs will significantly increase!
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
HDDs excel in scenarios requiring maximum storage capacity at minimum cost1213. Their primary applications include:
- Mass storage and backup systems - Ideal for storing large amounts of infrequently accessed data
- Media libraries and archives - Perfect for storing photos, videos, and documents for long-term retention
- Surveillance systems - Excellent for continuous recording applications where capacity matters more than speed
- Budget-conscious builds - Suitable for users prioritizing storage space over performance
SATA SSDs
SATA SSDs provide an excellent balance of performance and affordability1314, making them suitable for:
- General computing and office work - Significantly faster boot times and application loading
- Gaming systems - Reduced game loading times and smoother performance
- Laptop upgrades - Lower power consumption extends battery life while improving responsiveness
- Boot drives - Operating system and frequently used applications benefit from faster access times
NVMe SSDs
NVMe drives target performance-critical applications where speed is paramount1516:
- Content creation and video editing - Essential for 4K/8K video editing workflows and large file manipulation1617
- Professional workstations - CAD, 3D rendering, and data analysis applications benefit from maximum I/O performance18
- High-performance gaming - Eliminates loading bottlenecks in modern games with large asset files
- Enterprise servers - Database servers and virtualization platforms require maximum throughput and low latency
Power Consumption and Reliability
Power consumption varies significantly between storage types. HDDs consume 6-9 watts during active use due to their mechanical components, while SATA SSDs require only 2-3 watts1920. NVMe drives consume 3-10 watts depending on generation, with newer PCIe 5.0 drives using more power during peak performance21.
Reliability metrics show enterprise-grade drives achieving Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) ratings of 1-3 million hours across all technologies22. SSDs and NVMe drives benefit from no moving parts, reducing mechanical failure risks compared to traditional HDDs23.
Recommendations for Different Users
Budget-conscious users should consider HDDs for bulk storage combined with a small SATA SSD for the operating system. For homelab users building a media server, these are great choices to house your media library. General users and gamers will find SATA SSDs provide the best performance-to-price ratio for most applications. Professional users and content creators should invest in NVMe PCIe 4.0 drives for optimal workflow performance, while cutting-edge applications may justify PCIe 5.0 technology.
The choice between storage technologies comes down to balancing performance requirements, capacity needs, and budget constraints. Now that you know a little more about how these technologies compare you can make an informed decsion based on your use case.
https://www.soladrive.com/hard-drive-vs-ssd-vs-nvme/
https://superuser.com/questions/1633000/max-read-write-speed-of-a-sata-3-0-hdd-rated-at-6-0gb-s
https://americas.kioxia.com/en-ca/business/resources/tech-brief/good-better-best-ssd.html
https://www.sabrepc.com/blog/Computer-Hardware/nvme-ssd-vs-sata-ssd-vs-hdd
https://www.reddit.com/r/techsupport/comments/187bs4a/which_is_my_actual_hdd_readwrite_speed/
https://ssd-tester.com/sata_ssd_test.php
https://www.reddit.com/r/buildapc/comments/1hnz43s/m2_nvme_vs_sata_ssd_speed_difference_in_practice/
https://www.teamgroupinc.com/community/en/blog-detail/basic-knowledge-ssdvshdd/
https://www.reddit.com/r/Amd/comments/cb9lae/pcie_gen_4_m2_max_speeds/
https://www.seagate.com/blog/recommended-storage-for-gaming-pc/
https://superuser.com/questions/1170411/what-kind-of-periodic-maintenance-should-i-carry-out-on-hdd-backup
https://www.kingston.com/en/ssd/kc3000-nvme-m2-solid-state-drive
https://www.seagate.com/products/gaming-drives/
https://www.reddit.com/r/Backup/comments/1dbyj7k/which_type_of_external_backup_drivessystems/
https://www.atpinc.com/products/industrial-gen4-nvme-M.2-ssd
https://www.reddit.com/r/AskTechnology/comments/1daju22/use_cases_for_hdd_drives_for_home_office_and/
https://www.tomshardware.com/news/backblaze-expects-one-cent-per-gb-hdds-by-2025
https://www.promax.com/blog/what-is-the-best-storage-size-for-video-editing
https://www.enterprisestorageforum.com/management/types-enterprise-storage/
https://diskprices.com/?locale=uk
https://www.seagate.com/blog/how-to-do-storage-for-video-editing-right/
https://www.dell.com/en-ca/shop/scc/sc/storage-products
https://diskprices.com/?locale=ca